Technology
Technology
Science produces many new theories of which new materials or methods could revolutionise the world. Some of which contribute to a more eco-stable environment.

Biodegradable plastics.
One of the more visible changes that the modern world has on the world, is its plastic footprint. This is shown in the massive landfill, the large recycling, but more the waste that is dumped in nature. The plastic soup in the oceans covers about 700.000m3 - 15.000.000m3 and has an unknown mass. The estimated yearly global damage is about 20 Billion € with possibly more damage in the future.[4][5][6]
Plans are being put into motion to clean these garbage patches. But it is for now not more than a drop in the ocean, as plastic is continuously being dumped. If plastic could break down like any other nutrient, there would be no real problem. But a biodegrabable plastic ages more quickly, how do you create a plastic that is strong, durable but is also biodegradable.

The "great" pacific garbage patch.

Additives
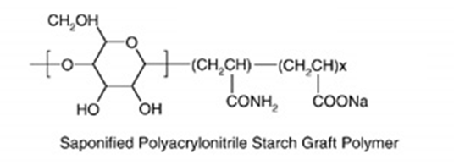
To make a non-biodegradable plastic into a biodegradable plastic, additives are used to give bacteria a chance to digest the mixture. [7] Additives could be a hydrophylic sugar or lipid. However its function as a best alternative is debated. Starch based bioplastics under the right conditions is entirely reduced to water and carbonmonoxide. However this material lacks durability. [8]

Arthropods
Chitin from arthropods, is a durable and strong material that is similar to most plastics, it is somewhat heat resistant, and extremely flexible.
Also collagene (tendons & skin) and creatine (hair) are candidates to create the ideal biodegradable plastic from. However mass production or creating fibers from the already formed substances is very difficult, though sound in theory.

Molecular structure, starch polymer.